Neuroscience of NFTs: How Digital Collectibles Affect Your Brain

NFTs (non-fungible tokens) have taken the digital world by storm, transforming art, collectibles, gaming, and more. But beyond the hype and market dynamics lies a fascinating area of study: how owning and interacting with NFTs influences the human brain. Neuroscience of NFTs and psychology reveal intriguing insights into the cognitive and emotional effects of digital collectibles, shedding light on NFT user behavior, decision-making, and motivation.
The Brain Science Behind NFTs and Digital Collectibles
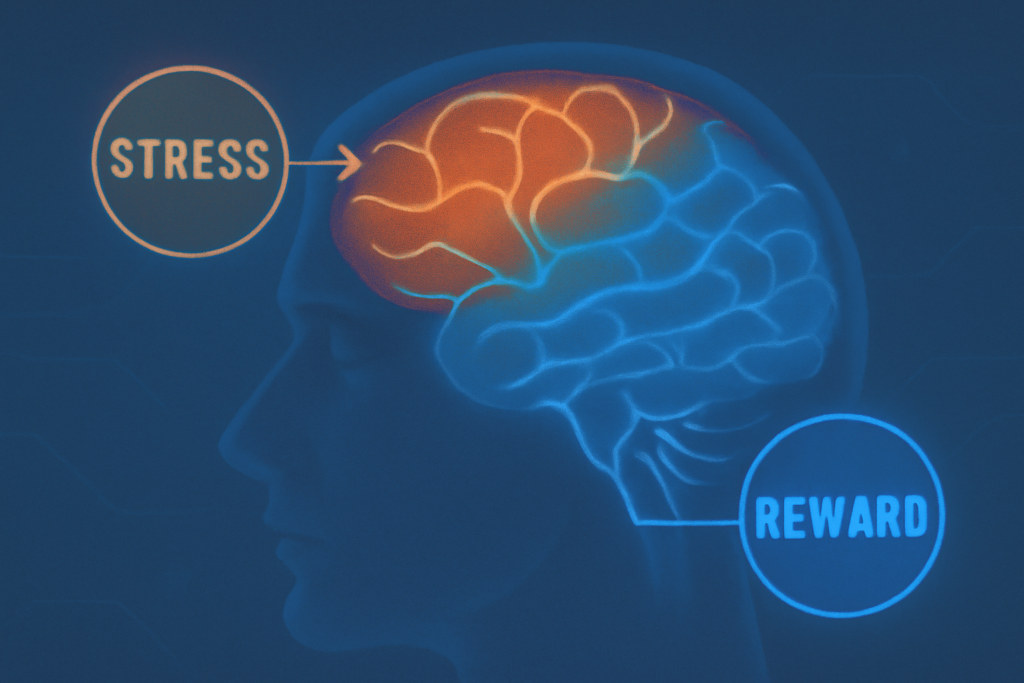
At their core, NFTs are unique digital assets recorded on blockchain, but their psychological impact goes beyond technology. The brain processes NFTs similarly to physical collectibles due to their uniqueness, ownership proof, and social status signaling. This taps into neural circuits related to reward, memory, and social cognition.
Owning NFTs can activate the brain’s reward system, releasing dopamine when acquiring rare or valued digital assets. This neurochemical response reinforces behaviors such as collecting, trading, or displaying NFTs.

Emotional and Cognitive Responses to NFT Ownership
Emotional attachment to NFTs arises from their perceived value and rarity. This emotional connection can be linked to the brain’s limbic system, which governs emotions and memory formation. For many, NFTs serve as digital trophies that boost self-esteem and identity expression.
Cognitively, interacting with NFTs involves complex decision-making processes. The brain weighs risks and rewards when buying or selling NFTs, engaging the prefrontal cortex responsible for executive function and impulse control.
Blockchain Psychology and Social Identity in NFT Communities
NFTs also create unique social dynamics. Being part of NFT communities can fulfill social needs for belonging and recognition, activating social cognition networks in the brain. These communities often drive collective behaviors, influencing investment and participation patterns.
Psychological studies show that blockchain identity, linked with NFTs, can affect users’ self-concept and digital presence, contributing to how they value their assets and interact within ecosystems.

NFT Behavioral Science: How NFTs Influence Decision-Making
NFT buying and selling involve behavioral economics principles. The scarcity effect and fear of missing out (FOMO) can trigger strong impulses, sometimes overriding rational choices. This is linked to the brain’s amygdala and emotional processing centers.
Additionally, cognitive biases like anchoring and confirmation bias influence NFT valuation and trading decisions. Understanding these behaviors helps platforms design better user experiences and protect consumers from impulsive risks.
Psychological NFTs: Potential Mental Health Implications
While NFTs can enhance engagement and enjoyment, excessive involvement or speculative behavior may contribute to stress, anxiety, or addiction-like symptoms in some individuals. Researching into Neuroscience of NFTs and compulsive digital asset trading is emerging, highlighting the need for awareness and responsible platform design.
Mental health experts suggest balancing NFT participation with mindful practices and community support to mitigate negative psychological effects.
Cognitive Science Innovations: NFTs in Learning and Memory
NFTs may also have positive cognitive applications. Their ability to create memorable digital artifacts opens avenues for education and knowledge retention. Tokenized certificates, badges, or achievements linked to blockchain can enhance motivation and memory encoding through reward-based learning.
Emerging studies explore how NFT-based gamification in education can stimulate brain plasticity and improve cognitive outcomes.
Neuroscience of Trust and Authenticity in NFT Transactions
The blockchain’s transparency and immutability foster trust, which plays a critical role in how the brain processes NFT ownership. Trust activates the brain’s reward and social cognition regions, reinforcing feelings of security and legitimacy in transactions. This sense of authenticity boosts user confidence, encouraging more active engagement and investment in NFTs.
Platforms that leverage these neuroscience insights by offering verifiable provenance and transparent ownership records help users feel more connected and assured.
The Role of Novelty and Surprise in NFT Engagement
Neuroscience of NFTs shows that novelty and surprise stimulate dopamine release, enhancing attention and learning. NFT drops, limited editions, and rare collectibles capitalize on this by creating anticipation and excitement. This mechanism drives user engagement, motivating collectors to seek out new and unique tokens actively.
Understanding this brain chemistry behind novelty can help NFT creators design experiences that maximize user satisfaction and retention without leading to addictive behaviors.
The Intersection of Memory and NFTs
Memory plays a crucial role in how individuals perceive value and form emotional bonds with NFTs. Neuroscientific research suggests that NFTs, as digital artifacts, can serve as mnemonic anchors that trigger recollection and personal meaning. For instance, owning a particular NFT can evoke memories tied to a community event, artist, or moment in digital culture.
The hippocampus, a key brain region involved in memory consolidation, is activated when individuals engage with personally significant NFTs. This neurological engagement can deepen the sentimental value of digital collectibles beyond their market price.
How NFTs Influence Consumer Behavior
From a behavioral neuroscience perspective, NFTs influence consumer behavior through mechanisms related to reward anticipation and social comparison. The competitive nature of NFT markets taps into the brain’s reward pathways, encouraging users to seek status-enhancing collectibles.
Social media and NFT marketplaces amplify these effects by providing constant feedback loops, including likes, shares, and peer validation. This social reinforcement activates the ventral striatum, enhancing motivation and sustained interest in NFT collections.
Potential for Cognitive Overload and Digital Fatigue
While engaging with NFTs can stimulate positive neural pathways, excessive exposure may also lead to cognitive overload. The constant influx of NFT drops, updates, and market fluctuations can tax working memory and attention systems, leading to digital fatigue.
Neuroscience highlights the importance of balancing engagement with rest to maintain cognitive health. NFT platforms incorporating features that manage notifications and promote mindful use can help mitigate these challenges.
Ethical Considerations: Neuroscience-Informed NFT Design
As the understanding of NFTs’ impact on the brain grows, ethical design becomes paramount. Integrating neuroscience principles into NFT platforms can promote healthier user experiences by minimizing addictive patterns and enhancing informed decision-making.
Developers can incorporate cognitive nudges, transparency in risk communication, and tools that support emotional regulation. This ethical approach ensures that NFTs serve as enriching digital assets rather than sources of harm.
ALSO READ: NFT Algorithms and Smart Contracts Empowering Digital Art
FAQs
Q1: How do NFTs affect the brain’s reward system?
A1: NFTs can trigger dopamine release, reinforcing behaviors linked to collecting and trading digital assets.
Q2: Can NFTs cause addictive behaviors?
A2: Excessive NFT trading might lead to stress or compulsive behaviors, but responsible use and awareness help mitigate risks.
Q3: What role does social identity play in NFT communities?
A3: Social belonging and recognition in NFT groups activate social cognition areas, influencing user engagement and value perception.
Q4: Are NFTs useful for education and memory?
A4: Yes, NFTs can enhance motivation and learning by linking rewards to knowledge retention and gamified experiences.
Call to Action (CTA)
🧠 Dive deeper into the fascinating world of neuroscience of NFTs! Subscribe now for the latest research, insights, and innovations shaping digital collectibles and brain science.